The Internet of Things allows millions of devices to be connected, measured and monitored to automate processes and operations and support better decision making. The soaring of the Internet of Things is supported by the Low–Power, Wide-Area Networks (LPWAN) allowing the transfer of information at low cost. Many technologies and communication protocols co-exist on the IoT market for different applications. Industrial IoT demands cost-effective, long-range and power-efficient sensors and actuators. LoRa® and LoRaWAN® stands out by optimizing LPWAN for the battery lifetime, capacity, range, and cost.

Learn more about the LoRaWAN technology by downloading the Actility “What is LoRaWAN” white paper
For more technical details and resources:
The advantage of LoRa® is its long-range capability. A single gateway or base station can cover entire cities or hundreds of square kilometers. Range highly depends on the environment or obstructions in a given location, but LoRa® – and its MAC layer LoRaWAN™ – have a link budget greater than any other standardized communication technology. The link budget, typically given in decibels (dB), is the primary factor in determining the range in a given environment.
The LoRaWAN™ protocol is a global standard that offers a long range (up to 15km) bi-directional communications with very low power consumption, allowing operation for up to ten years on the same battery. LoRaWAN™ is using the unlicensed ISM (Industrial, Scientific, Medical) radio bands for cost-efficient network deployments.
LoRaWAN provides long-range (up to 15km) communication between sensors and base stations, resulting in networks with 2-3x times fewer base stations compared to cellular.

LoRaWAN data transmission and reception requires low current (less than 50 mA), dramatically reducing power consumption of the devices and allowing a battery life of up to 10 years.
Fully bidirectional communication enables a wide variety of uses cases requiring uplinks and downlinks: for example, street lighting, smart irrigation, energy optimization or home automation.
The LoRa radio modulation allows deep indoor penetration and adds the ability to reach sensors monitoring water or gas meters located underground.
The LoRaWAN standard is based on an open protocol approach managed by the LoRa Alliance which supervises the development of the standard and ensures interoperability between all LoRaWAN networks.


LoRaWAN networks are deployed on cost-free ISM bands (EU 868, AS 923, US 915 Mhz) allowing any service provider to deploy and operate LoRaWAN networks without having to acquire a license for any frequency.
The LoRaWAN open standard combined with cost-free operation frequencies and low-cost base stations allows operators to roll out networks in a just few months and with minimum investment.

LoRaWAN can use network triangulation to passively locate any LoRa device. This enables new tracking applications, lower cost, and better battery life optimization if compared to GPS.
A typical LoRaWAN network uses a simple architecture where LoRaWAN base stations connect to the internet through a variety of available backhauls and manage the bidirectional data flow between LoRa sensors and the centralized ThingPark network server provided by Actility.
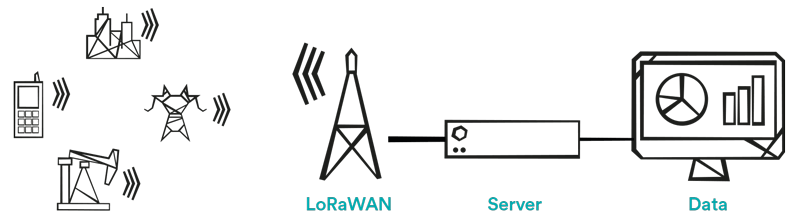
LoRaWAN networks enable a large variety of vertical solutions allowing service providers to use one platform and standard to manage various use cases such as intelligent buildings, precision agriculture, smart metering or smart cities.

Smarter grids
Enhancing networks

Maximising efficiency

Optimizing production

Smart supply chain

Intelligent management
Empowering growth
Citizen satisfaction
The LoRaWAN protocol is actively supported by the LoRa Alliance, an open and non-profit association of members. It is the fastest growing tech ecosystem in the technology world, with over 500 members, including mobile network operators, base station suppliers, sensor manufacturers, and system integrators.


Learn more about the LoRaWAN technology by downloading the Actility “What is LoRaWAN” white paper